Python code
Repository - Python code can be downloaded or cloned from the repository at https://github.com/roni-polymod/models.git
Dependencies - svgwrite module is required to run the code - install instructions at https://pypi.org/project/svgwrite/
the module is only referenced in one function, write_svg_file in write_model_file.py so if you have a better svg writing module it can be easily substituted.
Usage
$ python write_model_file.py [-h] [-n FILENAME] [-a] [-f] [-e] poly stkey
Write SVG file for polyhedron face or edge models
positional arguments:
poly polyhedron name
stkey dict key to size, type and repeat parameters
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-n FILENAME, --filename FILENAME relative path and file name to save, (default polyhedron name.svg in current folder)
-a, --array True for array repetition of pieces, default to single piece
-f, --face Face model (default)
-e, --edge Edge model (no effect if -f also used)
Examples
$ python write_model_file.py cube 5e
will create a single face for a cube with 50mm edge (5e size and type key parameter). The file will be saved as cube.svg in the working directory.
$ python write_model_file.py tetrahedron 5r -n files/edges.svg -ae
will create an array (-a option) of edge struts (-e option) for a tetrahedron with 50mm circumradius (5r size/type key parameter). The file will be saved as edges.svg in the files subdirectory directory.
dictionary parameter examples
The polyhedron name, 'cube' in the above examples, the size/type key and the array repetitions are set in the polyhedrondict dictionary in param_dictionaries.py.
You can look at the comments and other dictionary entries there to see the polyhedra that are available and use a similar format to add to the code if you wish. Two example dictionary entries are shown below for illustration.
polyhedrondict = { 'face_cube': {'5e': (square, 50, 10, 3, 58, 2, 58), '5r': (square, 57.74, 12, 3, 65.5, 2, 65.5)}, . . 'edge_tetrahedron': {'5e': (50, 30, 30, 'P', 4, 50.5, 3, 18.5), '5r': (81.65, 30, 30, 'P', 2, 82, 3, 18.5)} . . }
Face model call:
$ python write_model_file.py cube 5e
Accesses the 'face_cube' key, as face is the default type, and then the '5e' key inside to return the tuple (square, 50, 10, 3, 58, 2, 58). The parameters
in the tuple represent respectively:
function name to be called to draw the polygon shape - e.g. square edge length - e.g. 50mm end tab length - e.g 10mm (see diagram below) array repetition parameters cols, x, rows, y - e.g. 3 columns 58mm horz spaced and two rows 58mm vert spaced but note that in this case as the -a parameter is not given, only a single square is drawn
These parameters are combined with more from the face parameter dictionary which gives finer settings for the tabbed edges of the polygon faces as shown in the diagram below. Click to see full diagram.
faceparamdict = {'ta': 3.5, 'if2': 0.1, 'so': 0.25, 've': 1.0, 'isl': 1.0, 'etc': 2.0, 'theta': 30, 'tab_type': 1}

tab_type 1 is shown in the image. tab_type 0 is a simple straight edge with no tabs or scores which allows creation of plain polygons.
The parameter values work for the 250gsm card that I have been using. They have been arrived at by trial and error so I can't say they are optimal but they work for my materials. You may be able to get better results or ease of assembly by experimenting with the parameter values or creating your own tab types.
You can see the other models that can be called from the cli and add more of your own by examining the polyhedrondict code. Currently the face models are:
cube, tetrahedron, octahedron, icosahedron, dodecahedron with type 5e or 5r
-
custom - various types often with extra parameters which are handled individually in the code. You will have to look at the code for details and possibly modify values within the custom routines, briefly the types available are:
5e: regular polygon with an extra parameter for number of sides to create octagons, decagons or any other n sided regular polygon
tr_custom - irregular triangles
tr_nscored - option to score only 1 or 2 of the edges, used for non convex models
great_dodec - great dodecahedron faces
simple_quad - simple quadrilateral
quad - irregular quadrilateral, used for the kaleidoscope experiments with tab type 4
rhombicdodecahedron, rhombohedron, rhomb_tile - rhombus routines with an extra rhombus theta (angle) parameter for the rhombic models. rhombicdodecahedron has the sqrt2 diagonal ratio rhombus and rhombohedron the golden ratio diagonal
catalan - options for two of catalan models, Pentagonal icositetrahedron or Deltoidal icositetrahedron
propeller_unit - faces based on unit origami designs, tab joins within the faces rather than at the edges
test - test strips to experiment with tab design variations
Edge model call:
$ python write_model_file.py tetrahedron 5r -n files/edges.svg -ae
Accesses the 'edge_tetrahedron' key (-e option), and then the '5r' key inside to return the tuple (81.65, 30, 30, 'P', 2, 82, 3, 18.5). The parameters
in the tuple represent respectively:
edge length - e.g. 81.65mm angle thetaL - 'left' end angle 1 e.g. 30 degrees angle thetaR - 'right' angle 2 e.g. 30 degrees vertex type - e.g P for platonic, also possible are A for archimedean and R for Rhombic array repetition parameters cols, x, rows, y - e.g. 2 columns 82mm horz spaced and 3 rows 18.5mm vert spaced
Only one strut routine is needed for all models as it is the end angles and arrangement of the vertices that produce the required struts. This is the asym_strut_lf routine in strut_routines.py.
The above parameters are combined with more from the strut parameter dictionary which gives finer settings for the tabs and slots of the edge model strut as shown in the diagram below. Click to see full diagram.
strutparamdict = {'w': 7.5, 'ta': 3.0, 'tt': 0.4, 'ss': 2.0, 'twf': 0.85}

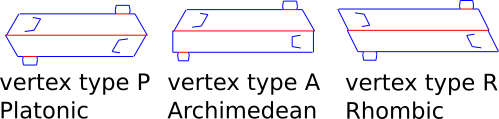
The example above shows vertex type P for the edge of a platonic model. Archimedean models have different polygons on either side of each edge. This is achieved by using different left and right end angles and transposing these about the edge. Rhombic models have the same polygons but different vertex figures which is achieved by a different transposition of the ends. The image below shows typical platonic, archimedean and rhombic struts.
Currently the edge models in polyhedrondict are:
cube, tetrahedron, octahedron, icosahedron, dodecahedron with type 5e or 5r
archimedean with type 5r, set the left and right angle parameters to get the different archimedean edge struts
rhombicdodecahedron wity type 5e or 5r (very little difference)
rhombohedron - struts of the rhombic model set based on the golden ratio diagonal rhombus. Types 5eP, 5eR1, 5eR2 for the different vertex types required, platonic and rhombic in a left and right handed form
pentagonal_icositetrahedron with types 5eShort and 5eLong for the long an short edges of the catalan models
Code overview and combining models in a single SVG
point_routines.py handles basic points, paths and drawing layers used in the other routines. strut_routines.py for the edge struts and face_routines.py for the faces polygons with tabbed edges. write_model_file.py provides the interface to call the other routines and write the svg files.
If you wish to create svg files with different model pieces combined on them programmatically, this cannot be done in the cli but can be done from the code by using the routine combine_svgs in write_model_file.py. This was used to write the saved A4 svg files. Look into the code for examples of how to chain svg drawings together.
Copyright on the code
None, use as you wish but please do share anything interesting.